Overview
There are three main types of deadbolts:
- Tubular (or Cylindrical)
- Rim (surface mount)
- Mortise
This article discusses the installation details and relative merits of each, as well as what to look for in terms of quality and security.
Deadbolts are usually considered an auxiliary lock because, with the exception of aluminum and glass storefront doors, they are not the primary means of latching the door shut.
Tubular Deadbolts
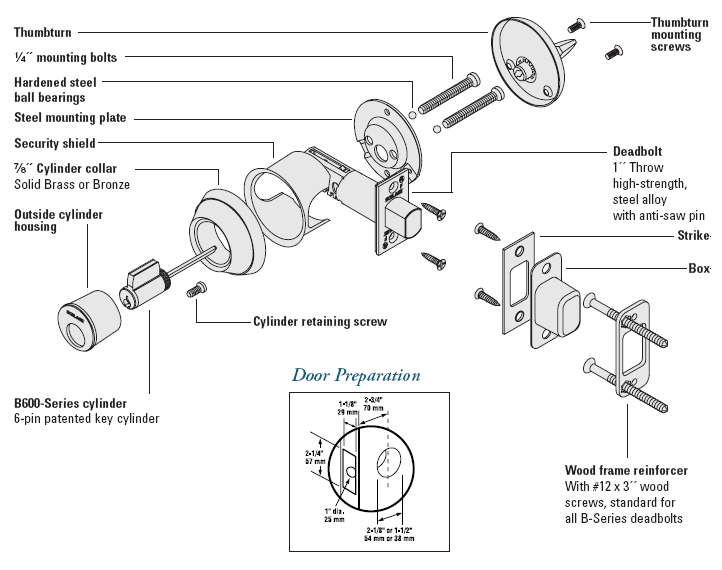
Above is a the first page of the B600 Series section of the Schlage commercial price book, showing an exploded view of the B600 series deadbolt. Notice the “Security Shield” that protects the bolt from attack through the door.
Tubular (or cylindrical) deadbolts are by far the most popular deadbolts used today. Preferred by renovation contractors for their ease of installation, they differ greatly in quality and security.
Installation
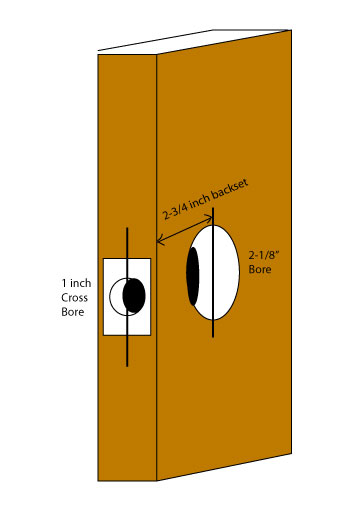
Tubular (or cylindrical) deadbolts are generally installed into a modified 161 door prep – that is, the same prep that accepts a standard cylindrical doorknob or lever set. The 161 prep consists of a 2-1/8 inch diameter hole drilled through the door. This hole is called the “bore.” A second hole, called the “cross bore,” is then drilled from the lock edge of the door to intersect with the bore. This second hole is usually 7/8 or 1 inch in diameter and is located on the center line of the first hole. See diagram:
Quality and Security
Quality in tubular deadbolts ranges from the relatively poor quality of inexpensive locks widely available in lumber yards and hardware stores to high security versions available mainly from locksmiths and other security hardware specialists. The differences between cheap and good are:
- Sturdiness of the bolt
- Strike reinforcement
- Guarding of the bolt
- Sturdiness of the cylinder collar
- Bump, pick and drill resistance
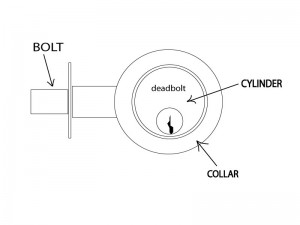
The bolt is the actual part that projects out of the door and into the door frame. The sturdier it is, the harder it will be for a burglar to break it off or saw through it.
 The strike, or strike plate, is the rectangular piece of metal in the door frame that receives the bolt. In a wooden frame, this piece will only be as strong as the wood it is attached to. This is why it is important that the strike fasteners are long enough to reach the stud behind the frame.
The strike, or strike plate, is the rectangular piece of metal in the door frame that receives the bolt. In a wooden frame, this piece will only be as strong as the wood it is attached to. This is why it is important that the strike fasteners are long enough to reach the stud behind the frame.
The dust box goes inside behind the strike plate, inside the door frame. A metal dust box makes it much more difficult to get a tool behind the end of the bolt – a very important function in terms of burglary resistance.
On a steel door frame the strike plate becomes less important, but it is still important to guard the end of the bolt as effectively as possible.
The cylinder collar is the washer-like ring that surrounds the cylinder and rests against the exterior surface of the door. The best deadbolts have solid collars that spin freely if one tries to twist them off with pliers. Cheap deadbolts have hollow collars that crush like a beer can when gripped by pliers.
Since key bumping videos are now widely available via the Internet, it is worthwhile making sure your locks are bump resistant; lock picking is more of an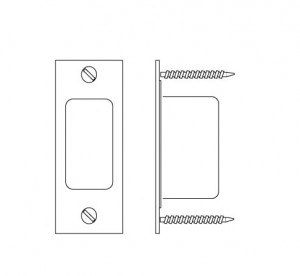 art, but some burglars are skilled in it, so pick resistance is worth having; and because cordless drills are inexpensive and readily available, drill resistance is a good thing, too. Locks that are resistant to these three kinds of attacks have a UL Listing UL437 for Burglary Resistance and say so on their labeling. Two deadbolts that offer UL437 burglary resistance as well as sturdy bolts, collars and provisions for strike reinforcement are the Schlage B600 series with Primus or Everest UL437 cylinder, and the Medeco D11 series with M3 series cylinder.
art, but some burglars are skilled in it, so pick resistance is worth having; and because cordless drills are inexpensive and readily available, drill resistance is a good thing, too. Locks that are resistant to these three kinds of attacks have a UL Listing UL437 for Burglary Resistance and say so on their labeling. Two deadbolts that offer UL437 burglary resistance as well as sturdy bolts, collars and provisions for strike reinforcement are the Schlage B600 series with Primus or Everest UL437 cylinder, and the Medeco D11 series with M3 series cylinder.
Rim Deadlocks
The terms “deadlock” and “deadbolt” are often used interchangeably.
Surface mounted deadbolts, AKA rim deadlocks, were once the industry standard. Many locksmiths’ fortunes were made on the Segal 667 “jimmy proof” deadbolt with cylinder and latch guards, and, in fact, that locking system was often effective in keeping burglars out. My personal preference for maximum locking strength (short of a multi-point lock) is a jimmy proof rim deadbolt and a tubular deadbolt on the same door.
Here is an illustration of the Segal vertical deadbolt:
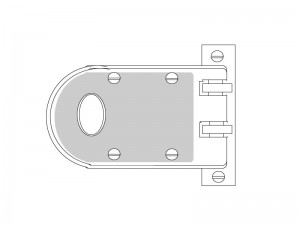
A jimmy proof deadbolt, otherwise known as a vertical deadbolt, is the most effective kind of rim deadlock because it interlocks the door and frame in a way that few other locks do.
The other kind of rim deadlock is a horizontal deadbolt such as the Yale 112 (see below left).
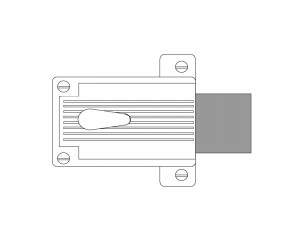
The Yale 112 features a 1-1/2 inch throw deadbolt – ½ inch longer than what is normally available in a tubular deadbolt.
To achieve bump, pick and drill resistance in a rim deadlock, simply add a UL437 UL listed rim cylinder. Protect the cylinder with a cylinder guard to increase security still further.
The weakest part of the rim deadlock is the strike when it’s installed into a wooden frame. To help alleviate this weakness, install screws that are long enough to reach the stud behind the door frame.
On a metal frame, a rim lock strike can be very strong when it is installed correctly.
Mortise Deadbolts
There are two kinds of mortise deadlocks:
- Small Body Mortise Deadbolts
- Full Size Mortise Deadbolts
Small body mortise deadbolts are usually installed where most auxiliary locks are installed, six inches to a foot above the primary lock, maybe around 60 inches from the bottom of the door frame. The lock case of a small body mortise lock is variable – that is, it is not standardized.
A small body mortise deadbolt can be a good choice for a wooden door, especially if it is a thicker-than-usual wooden door. Since the lock is a good size metal box that gets tucked into an approximately 5 inch by 1/2 inch pocket carved into the wood, the lock utilizes the strength of the door to its best advantage.
Full size mortise deadbolts are installed in an “86 prep” (see illustration), 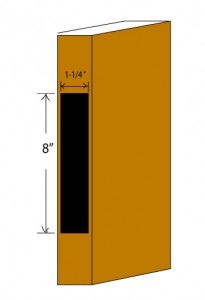 which is a pocket located on a center line about 40 inches above the bottom of the door frame. Unlike most other deadbolts, full size mortise deadbolts are intended for use as the primary – and usually the only – lock on any given door. Full size mortise deadbolts are usually used on mechanical compartments, closets in corridors or other places where trim would be in the way.
which is a pocket located on a center line about 40 inches above the bottom of the door frame. Unlike most other deadbolts, full size mortise deadbolts are intended for use as the primary – and usually the only – lock on any given door. Full size mortise deadbolts are usually used on mechanical compartments, closets in corridors or other places where trim would be in the way.
Both small body and full size mortise deadbolts feature heavy duty mechanisms and strong, 1-inch projection bolts. With the addition of a high security, UL437 UL listed mortise cylinder to add bump, pick and drill resistance, mortise deadbolts can provide a high degree of security.

Schlage L460 Series Small Body Mortise Lock
 The Securitech Lexi series retrofit exit device trim is available with a variety of back plates and adapters that allow it to be used with most major brands, including many surface vertical rod and concealed vertical rod exit devices. Compatibility with a variety of vertical rod devices is a major plus.
The Securitech Lexi series retrofit exit device trim is available with a variety of back plates and adapters that allow it to be used with most major brands, including many surface vertical rod and concealed vertical rod exit devices. Compatibility with a variety of vertical rod devices is a major plus. Installation instructions are easy to follow and short – only four pages, including the template. Something I would have liked to see in the instructions, but didn’t, was current draw. If I am installing one of these, the number of amps it draws are not going to matter much to me. But if I am installing twenty of them and want a centralized power source, now it’s an issue. Yet it isn’t anything that an experienced low voltage specialist with a ammeter can’t find out in two seconds.
Installation instructions are easy to follow and short – only four pages, including the template. Something I would have liked to see in the instructions, but didn’t, was current draw. If I am installing one of these, the number of amps it draws are not going to matter much to me. But if I am installing twenty of them and want a centralized power source, now it’s an issue. Yet it isn’t anything that an experienced low voltage specialist with a ammeter can’t find out in two seconds. As mentioned in the sales literature, since Securitech’s Lexi trim is compatible with so many exit devices, if you have a facility with different brands of exit devices dispersed throughout, you can install access control and unify the exterior appearance at the same time. And in addition to being versatile it is also durable. Forcing the lever only causes its internal clutch to break away, and it can easily be set right by rotating it back the other way.
As mentioned in the sales literature, since Securitech’s Lexi trim is compatible with so many exit devices, if you have a facility with different brands of exit devices dispersed throughout, you can install access control and unify the exterior appearance at the same time. And in addition to being versatile it is also durable. Forcing the lever only causes its internal clutch to break away, and it can easily be set right by rotating it back the other way.