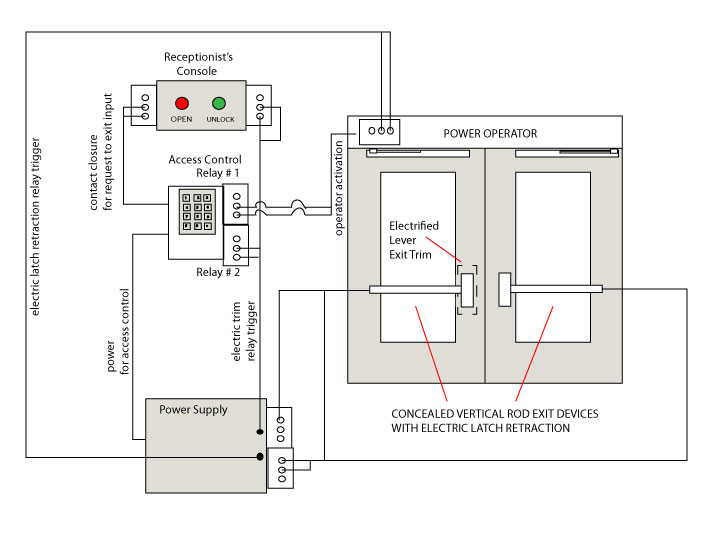
Delayed egress is a process that delays unauthorized exit from a space while complying with NFPA 101 life safety code. Use of this process is strictly regulated with the help of building inspectors and fire marshals across the United Sates. With that in mind it is always a good idea to get your local AHJ (Authority Having Jurisdiction) on board whenever you are planning to install delayed egress on an opening.
When you beginning planning your delayed egress system you will find that many systems on the market are self-contained. These could be delayed egress electromagnetic locks or electrified delayed egress exit devices.
Here are some examples of self-contained delayed egress maglocks:
- SDC 1511S
- Schlage Electronics M490DE
- Dynalock 3101C
Here are some examples of self-contained delayed egress exit devices:
- Detex V40 EE
- Von Duprin Chexit
- Sargent Electroguard
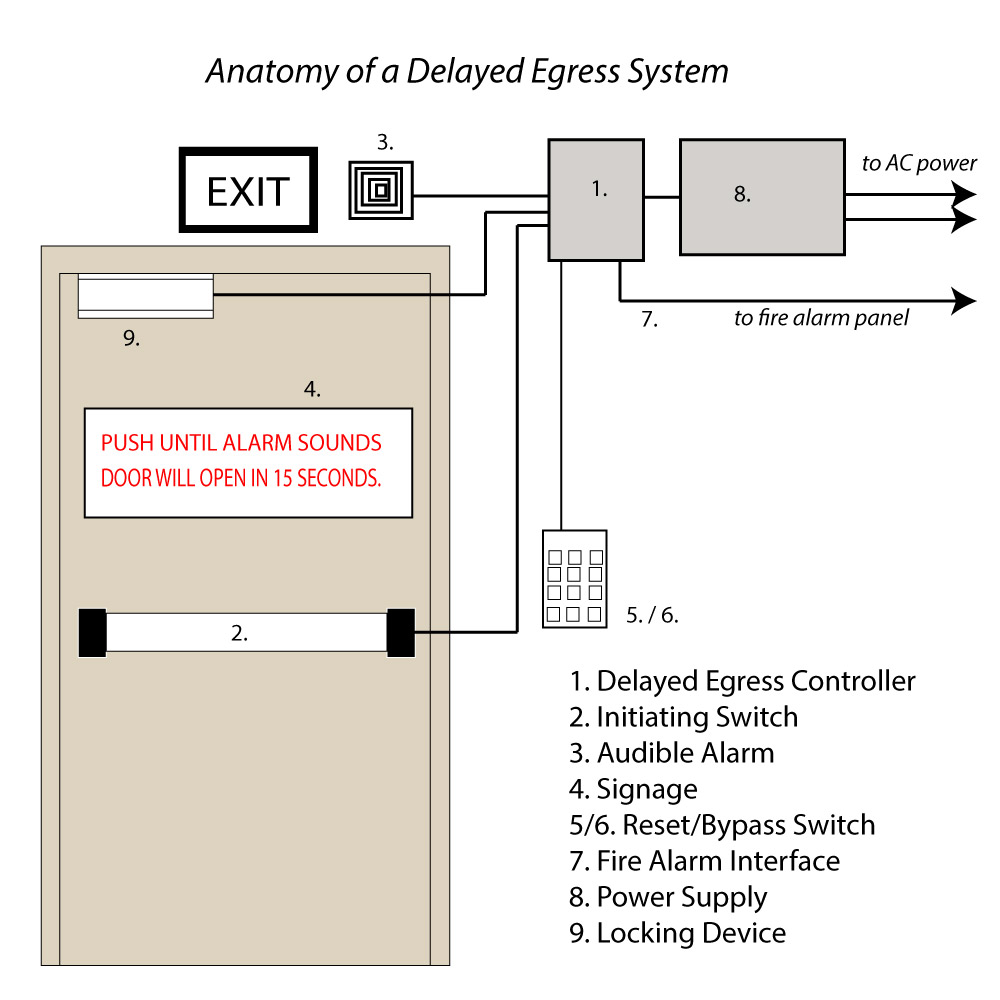
Almost all delayed egress systems are made up of the same components:
- Delayed egress timer and relay logic board
- Initiating Switch (to initiate the delayed egress process)
- Audible alarm
- Signage
- Reset switch
- Optional bypass switch
- Fire Alarm interface
- Power supply
- Locking device
Therefore it is possible to construct a custom delayed egress system from components. Later I’ll talk about why you might want to choose a built-from-components delayed egress system instead of a self-contained one. The following sections describe each part of a built-from-components delayed egress system.
Delayed Egress Timer and Relay Logic Board
This board is UL Listed and specifically designed to perform all delayed egress functions in compliance with life safety code. Here are some examples of component boards for delayed egress:
- Securitron XDT-12 or XDT-24
- Seco-Larm SA-025EQ
The board is the brains of the delayed egress operation. It has contacts to wire in switches for delayed egress initiation, fire alarm interface and system reset, timers to control nuisance and egress delay, and relays to control locks and notify external devices.
There are also delayed egress controllers that offer more features. The following may include the delayed egress timer/relay board and some other required feature(s) such as the initiation switch or the audible alarm.
- Alarm Controls DE-1
- Security Door Controls 101-DE
- Securitron BA-XDT-12 or BA-XDT-24
Initiating Switch
The switch that initiates the delayed egress process shares several characteristics with any request-to-exit switch. To comply with life safety regulations it must require no prior knowledge to operate; it must require no more than one motion to operate; and it must be placed in relation to the door according to life safety standards in your local jurisdiction. I think that the best possible initiation device is a mechanical push bar with a switch, such as the Adams Rite 8099-M or the Securitron EMB. In a panic situation it remains obvious that to get out, one must push on the bar, and because it is mechanical it is unaffected by power outage. If it is wired to open the contact when pushed, if the wires leading to it are cut it will initiate the delayed egress process.
In rare circumstances where it might be permitted, the locking device might be a fail safe electrified mortise lock that is locked on both sides, inside and out. Then the initiation switch might be a palm switch next to the door.
Audible Alarm
The mandatory audible alarm sounds for 15 seconds before the delayed egress controller releases the locking device to allow exit. It’s loudness must be between 81 and 88 decibels. In some jurisdictions the alarm must be manually reset at the door; in others it may be self resetting via timer or door position switch. Yet another reason to have a heart-to-heart talk with your local AHJ when designing your delayed egress system.
Signage
The wording on the mandatory sign must comply with life safety code. There are minor variations in wording. I suggest buying a sign that is part of a delayed egress system. The sign that comes standard with the Von Duprin Chexit is readily available as a separate part.
Reset Switch
As mentioned in the “Audible Alarm” section above, a delayed egress system reset switch located at the door is mandatory in some jurisdictions. Check with your local AHJ. In some jurisdictions delayed egress systems are allowed to be reset by remote switch or other means, such as a door position switch.
Any kind of momentary contact switch will do the reset switch job, but delayed egress system reset switches located at the door almost always require some kind of security to prevent unauthorized resetting. Standalone keypads or key switches are often used for this purpose. Delayed egress systems can also be integrated into existing access control.
Optional Bypass Switch
Not required but often needed, the optional bypass switch allows authorized personnel to exit without triggering the delayed egress system. Again, any momentary contact switch will do, but usually some security is required. If you are using a keypad as the system reset switch and the keypad has more than one relay, you can program the second relay to be the bypass switch.
If access from the exterior side is required a bypass switch is required on that side. Sometimes security is not needed from the exterior side. In that case a simple momentary contact pushbutton will do the job.
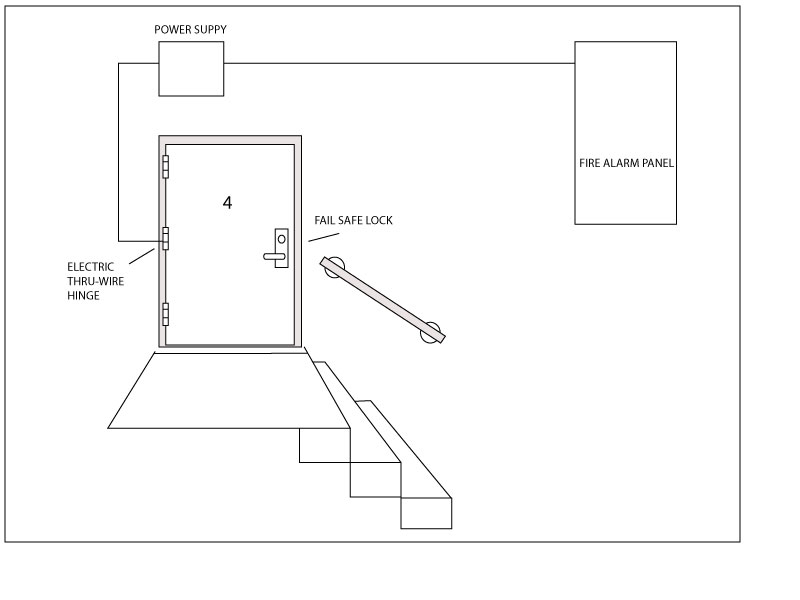
Fire Alarm Interface
The mandatory fire alarm interface allows enables fire alarm panel to deactivate the delayed egress system immediately in the event of a fire alarm. This is an integral part of the life safety code that allows a delayed egress system to exist. Therefore, if your building does not have a fire alarm panel, without special permission from the local AHJ you cannot have a delayed egress system.
Power Supply
All delayed egress systems I have had experience with run on low voltage power that comes from a low voltage power supply. Generally delayed egress systems require regulated and filtered power at 12 or 24 volts. Delayed egress controllers draw very little current, but as will all electrically operated systems, the current draw of all attached devices must be taken into account when selecting a power supply.
Locking Device
The locking device must be electrically locked and fail safe from the egress (interior) side. The most frequently used locking device in a component based delayed egress system is the electromagnetic lock.
Why Build a Delayed Egress System?
Why would you put together a delayed egress system from components when there are so many good self-contained systems?
- To Save Money. Piecing together a delayed egress system can be significantly cheaper than buying a self contained delayed egress system.
- To take advantage of existing hardware. For example, if there is already an electromagnetic lock on the door, adding the other components is relatively easy.
- Conditions at the door prohibit use of a self contained delayed egress system. For example, door size or the presence of existing hardware may require the installer to seek a more creative solution.
Bottom line, unless you have a prison, you cannot lock ’em in. Well, not without permission. 🙂